Artificial Intelligence: The Evolution and its impact on the future of work
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a hot topic of discussion among skilled and unskilled workers, with many speculating about its potential to take over jobs. As you may know, AI has already significantly impacted various industries worldwide. In this article, you'll learn about the evolution of AI and its positive effects on global industries while addressing some of this technology's concerns and negative impacts.
Overview Of Artificial Intelligence
Wikipedia refers to AI as intelligence demonstrated by machines, as opposed to intelligence displayed by non-human animals and humans.
Therefore, AI can be described as a field of computer science that focuses on developing computer systems (programs) that imitate intelligent human behavior such as learning, problem-solving, etc.
How Does Artificial Intelligence Perceive Data?
Janelle Shane and a group of coders at Kealing Middle School conducted an experiment where AI was given robot parts and asked to assemble and move from point A to point B, as shown in the illustration below:

It solved this problem by assembling itself into a tower and falling over to land at point B.
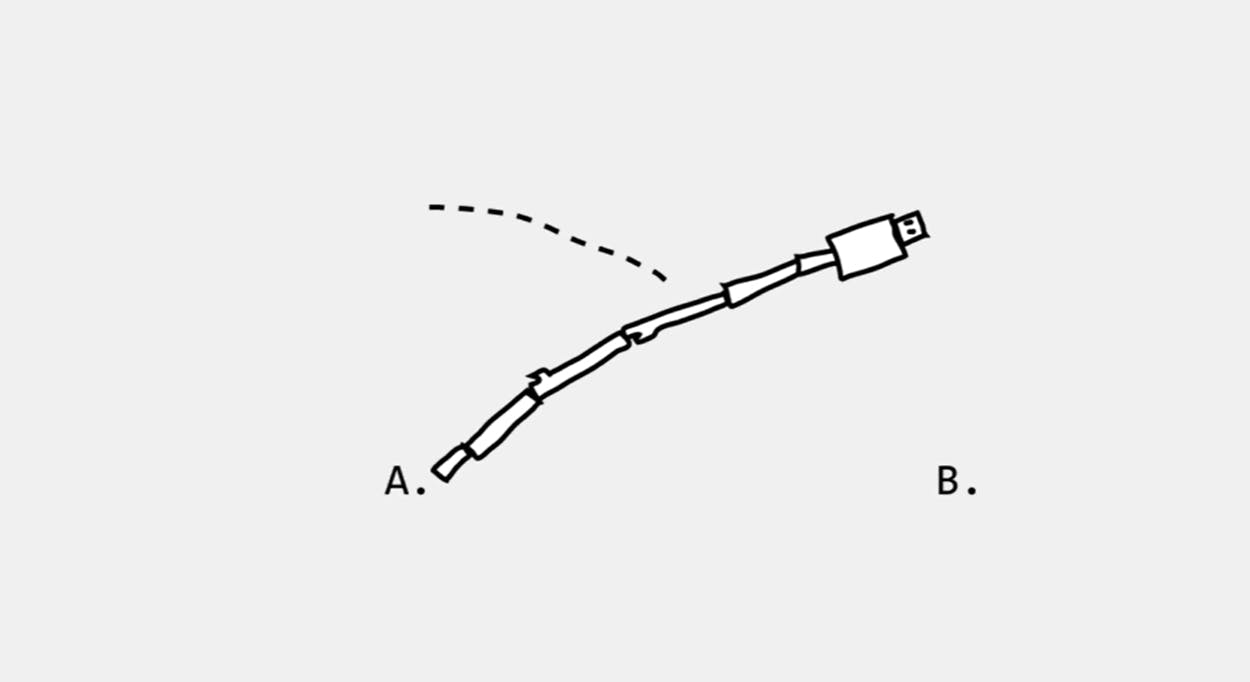
Technically, the problem has been solved because it reached point B. Now, AI won't be aware that the user wanted a program to assemble the bot and independently travel from point A to point B. Knowing how to set up a problem so that it does precisely what we want is an excellent key to working with AI.
Furthermore, AI can identify a person from a group of people. Still, it has no idea what that person is other than recognizing them as a collection of lines and textures - AI cannot identify the person as human in the way that another human would. The above scenario shows that AI is neither smart nor dumb; the data input often causes AI to do the wrong thing.
Evolution Of Artificial Intelligence
Modern-day artificial intelligence is a broad topic because AI has spread to different industries and is being used for several purposes. Some of these AI-related industries are:
The process of training computers to identify patterns and make predictions based on data is known as machine learning. It makes decisions based on statistical algorithms that improve in accuracy over time.
Natural Language Processing trains computers to understand and produce human words through techniques like speech recognition.
Robotics is the study of robot creation, construction, and management. Robots are made that can perform tasks in a variety of situations thanks to sensors and software.
Computer vision studies how a computer understands and evaluates visual data, such as images and videos. Object recognition, picture separation, and motion tracking are examples.
These are a few examples of the potential of artificial intelligence, which show that there is still room for AI to evolve. You can learn more about the fields surrounding Artificial Intelligence here.
Timeline Of Development Of Artificial Intelligence
Regardless of how complex the concept of AI and its surrounding fields seem, AI - like every living organism - grew over time. One could even say it evolved over the years.
British mathematician and logician Alan Turing recorded the earliest significant work on AI. He described an abstract machine that has limitless memory and a scanner. This machine stores a program in its memory as symbols that move the scanner back and forth, reading and writing more symbols. This theory is called the Turing Machine, and it implicitly describes the possibility of a machine operating on a program (instructions) given to it and improving its program as it does so.
Here are some significant early milestones AI has achieved over the years chronologically:
The first AI based program was written in 1951 by Christopher Strachey, director of the Programming Research Group at the University of Oxford. Strachey wrote a program for the game of checkers (draught), which ran on the Pilot ACE at the National Physical Laboratory but used up all the machine's memory. Later, Strachey went on to work with Alan Turing to transcribe his program into operations code that could be run by the Manchester Mark 1, which had a much bigger memory. In 1951, the Manchester Mark 1 played the game of checkers, and it also played chess rather quickly.
In 1956 Arthur Samuel demonstrated the fundamental concepts of AI on television when he showed off his checkers learning program, sometimes referred to as the "world’s first self-learning program". Samuel kept working on his program till the 1970s when the program was able to beat players of the amateur level.
Two years later, in 1958, American Scientist - John McCarthy introduced LISP, a language that made AI programming a reality. What made LISP special is that it was the first programming language that stored data in objects, not just as a list of items. An Object is a placeholder for data defined somewhere else in the program.
The following year American computer scientist Marvin Minsky and John McCarthy founded the MIT Lab, which focused on researching and developing AI. Because of its contributions to the growth of AI, the MIT Lab is considered necessary.
Moving on to 1964, the first demo of an AI program with the ability to understand natural language - ELIZA, was shown by Joseph Weizenbaum of MIT’s AI Laboratory. Eliza is a Natural Language Processing program that explores the difference between human and machine communications. It was designed to resemble a human therapist.
Fast forward to the 1980s, the first autonomous (self-driving) vehicles appeared, dating from research that had been ongoing since 1939. Research on computer-controlled vehicles began at Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) in 1984, and the production of the first vehicle, Navlab 1, began in 1986.
In 1989 Carnegie Mellon created the first autonomous vehicle using neural networks. ALVINN, which stands for Autonomous Land Vehicle In a Neural Network, was used by CMU around this period and into the 90s as a test vehicle. By the early 1990s, ALVINN could drive itself around the CMU campus, hitting speeds of 70mph.
1998 MIT AI Lab releases first-ever emotional AI Kismet. Kismet is capable of demonstrating social and emotional interactions with humans. It expressed how it felt with various facial expressions. Watch this video to learn more about how the Kismet robot reacts to different motions.
In 1999 Sony introduced Aibo, an autonomous four-legged entertainment Robot that acted in response to external stimuli and according to its judgment. Aibo could express emotions such as happiness and anger and instincts such as the need for companionship.
Google started working on its self-driving car project - Project Chauffeur, in 2009 and by 2010, it already had a modified Toyota Prius that could autonomously drive in city traffic and on highways.
2010 Siri was released as a stand-alone application for the IOS operating system with intentions from developers to make builds for both android and blackberry devices.
In February 2011, IBM's Watson defeated two human champions on the "Jeopardy!" quiz show. Watson was able to understand natural language questions and generate accurate answers.
In 2012, Google's X Lab developed a deep learning algorithm to recognize cats in YouTube videos. This development was particularly significant to facial and image recognition and other AI applications.
DeepMind's AlphaGo beat professional Go player Lee Sedol in the game of Go in 2015. This was the first time a computer beat a world champion at Go, which is much more complicated than chess.
By 2020, OpenAI had released the largest language model ever created, GPT-3, which has been used in many applications, including language translation and chatbots.
As time goes by, machines powered by AI and the abilities of these machines keep increasing ceaselessly.
The Impact Of Artificial Intelligence On Society
In present times, AI has contributed to world industries significantly. Some of these contributions are:
Healthcare: Artificial intelligence is applicable in areas like diagnosing diseases quickly and accurately, for example, PathAI. AI, such as da Vinci surgical systems, also aids surgeries.
Transportation: AI is used to optimize route planning during traveling, which helps reduce traffic congestion. Self-driving cars and trucks are also being developed using AI technology.
Agriculture: Agricultural activities have greatly improved since the inception of AI in areas like crop monitoring, precision farming, predictive maintenance, etc. It has made it easier for farmers to watch and manage crops, livestock, and equipment from the comfort of their homes.
Technology: AI has also helped the tech industry by improving existing products and services. For example, AI-powered algorithms enable analyzing large amounts of data to ensure informed predictions. Also, AI helps automate repetitive tasks such as data entry and customer service, in which case we can use chatbots as an example.
Artificial Intelligence And The Future Of Work
The rumor that "AI will take our jobs" is common gossip among skilled and unskilled workers. The fact staring us in the face is that AI will considerably impact the future of work. AI can take the place of repetitive tasks, which gives room for individuals to create and for brands to develop better marketing strategies. AI-powered tools also help in error reduction, increasing efficiency and productivity.
As good as it all sounds, it also means that automation will cause employment displacement for low-skilled workers who complete mundane, repetitive tasks. There is also the issue of workers becoming lazy and reliant on technology. All of this depends significantly on how AI is developed and used. When used right, it could add many jobs to the workforce and vice versa.
Wrapping Up
You've learned about how Artificial Intelligence processes data, AI's development over time, and its impact on the nature of work in the future. From its early days in the 1950s to today, AI has made tremendous progress in understanding and interpreting data.
However, the impact of AI on society has also raised important ethical and social questions. The widespread use of AI systems raises concerns about privacy, bias, and accountability. Remember that the AI revolution can be either good or bad depending on responsible usage and regulation, as the limits of Artificial Intelligence are continually tested.
I'm open to contributions and conversations around Artificial Intelligence and its impact. Please leave your comments or DM me on @twitter.
Thank you for reading 🤝